

Researchers used QDAS to support a variety of research designs and most commonly used the programs to support analyses of data gathered through interviews, focus groups, documents, field notes, and open-ended survey questions. The study found that the number of articles reporting QDAS is increasing each year, and that the majority of studies using ATLAS.ti™ and NVivo™ were published in health sciences journals by authors from the United Kingdom, United States, Neth-erlands, Canada, and Australia. This article reports the results of a content analysis of 763 empirical articles, published in the Scopus database between 19, which explored how researchers use the ATLAS.ti™ and NVivo™ QDAS programs.* The analysis specifically investigated who is using these tools (in terms of subject discipline and author country of origin), and how they are being used to support research (in terms of type of data, type of study, and phase of the research process that QDAS were used to support).
#DOWLOAD FREE ATLASTI SOFTWARE#
Qualitative data analysis software (QDAS) programs are well-established research tools, but little is known about how researchers use them. We provide systematic guidelines for novice IS researchers seeking to conduct a robust literature review. By viewing the literature review process as a qualitative study and treating the literature as the " data set ", we address the complex puzzle of how best to extract relevant literature and justify its scope, relevance, and quality. We contribute to the literature by proposing a four-phased tool-supported methodology that serves as best practice in conducting literature reviews in IS.
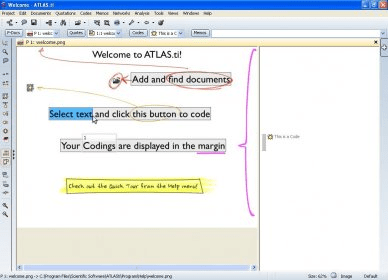
We discuss the means, value, and also pitfalls of applying tool-supported literature review approaches. We present a detailed case study as an illustrative example of the proposed approach put into practice.
#DOWLOAD FREE ATLASTI HOW TO#
In this paper, we describe how to organize and prepare papers for analysis and provide detailed guidelines for actually coding and analyzing papers, including detailed illustrative strategies to effectively write up and present the results. Qualitative data-analysis tools such as NVivo are immensely useful as a means to analyze, synthesize, and write up literature reviews. We highlight the untapped opportunities in using an end-to-end tool-supported literature review methodology. We overview work that has demonstrated the potential for using software tools in literature reviews.
Hence, a structured and efficient approach is essential. It is important for researchers to efficiently conduct quality literature studies. We illustrate this new framework through discussion of a collaborative action research project. Shifting the analytic focus from instrumentality and efficiency of QDAS to the research practice itself, we propose that qualitative researchers should formulate a "reflective space" at the intersection of their methodological approach, the built-in validity structure of QDAS and the specific research context, in order to make deliberative and reflective methodological decisions. This article suggests an alternative framework for examining the relationship between validity and the use of QDAS. It is a pressing issue, especially because the recent proliferation of conceptualizations of validity has challenged, and to some degree undermined, the taken-for-granted connection between the methodologically neutral understanding of validity and QDAS. However, very few discussions have developed regarding the effect of QDAS on the validity of qualitative data analysis. Qualitative data analysis software (QDAS) has become increasingly popular among researchers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
